Images
11/14/25About 11 min
Images
- When you set the
widthandheightof an image in CSS, it overwrites the settings of the HTMLwidthandheightattributes - In the example below:
- The first image has only
widthandheightattributes on theimgtag (400px*300px) - The second image (
#img2) has the samewidthandheightattributes on theimgtag (400px*300px), but in CSS thewidthandheightis set to200px*150px
- The first image has only
- CONCLUSION: As soon as you write the image dimensions in CSS, you may omit the
widthandheightattributes in HTML!
Responsive images
- Images sometimes have very annoying side effects, even with a proper
viewportmeta tag- Left: the
widthof the image is smaller than the viewport - Middle: the
widthof the image is larger than the viewport, so a horizontal scroll bar appears (when you touch the screen) - Right: the image is made responsive, which means that the image is scaled such that its
widthfits inside the screen's viewport
- Left: the
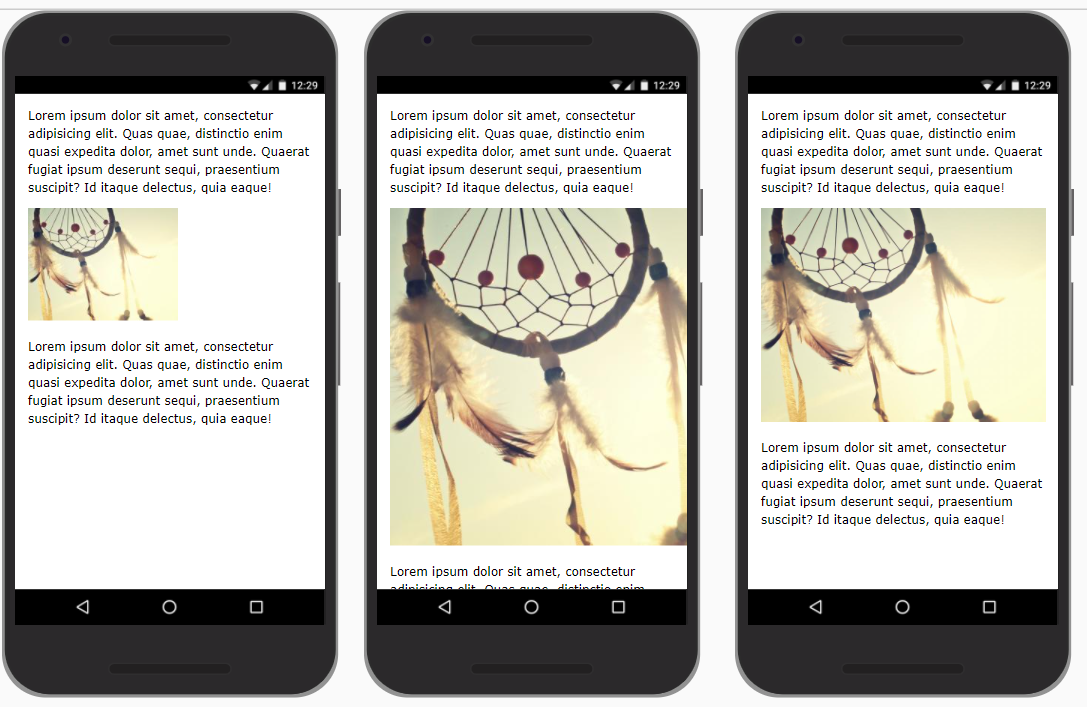
- For a responsive image, you set
- the
max-width(orwidth) to100%- Use
max-widthif the image width can't be larger than its originalwidth - Use
widthif the image width may be larger than its originalwidth(the image is enlarged/upscaled)
- Use
- the
heighttoauto
- the
img {
max-width: 100%; /* use `width` instead of `max-width` if the image is also allowed to scale up */
height: auto;
}- Open this pen in a new browser window to see the difference between the two images
REMARK
Be careful with width: 100% as upscaling images always comes with quality loss
Crop/resize images
- First, take a quick look at the example: images with different breakpoint
- On a small and large screen, all images are in landscape mode and are responsive
- On a medium screen, all images are in portret mode and have a fixed
widthandheight
- There are two ways to accomplish this:
- The hard way with Photoshop and JavaScript 😏
- Open Photoshop and make two versions for every image (a landscape version and a portret version)
- Add some JavaScript to switch between the different image versions at different breakpoints
- The easy way with pure CSS 😃
- Use the CSS property
object-fitto crop and/or resize the original image on different breakpoints - Use the CSS property
object-positionto position the cropped image
- Use the CSS property
- The hard way with Photoshop and JavaScript 😏
- Let's start with a simple example to explain these two properties
- Let's start with three images with different dimensions
- Left image:
270px*180px - Middle image:
600px*200px - Right image:
300px*500px
- Left image:
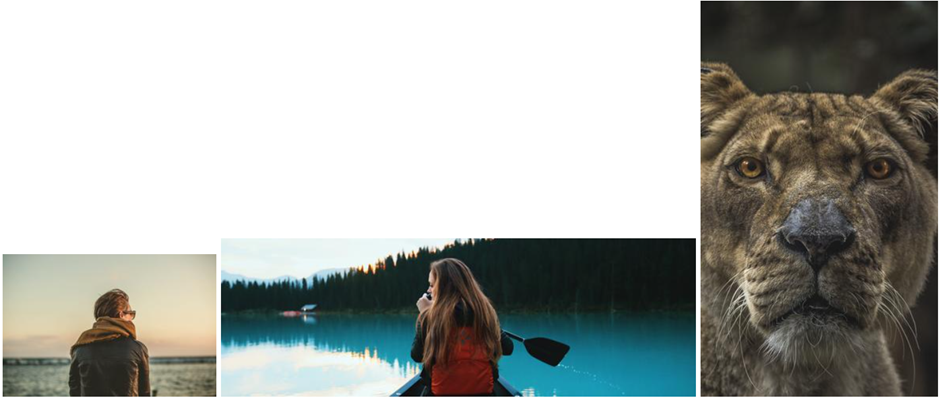

object-fit: fill (default)
- Give all images a fixed
widthandheight
img {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
}- Only the first image looks fine because it has the same aspect ratio as the CSS properties
- The two other images are scaled but squeezed/stretched to fit into the image box
- If you don't specify the
object-fitproperty, the browser usesobject-fit: fill;as the default setting

object-fit: contain
- All images are scaled to fit into the image box but maintain their original aspect ratio
img {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
object-fit: contain;
}
object-fit: none
- Only images that are larger than the box dimensions are scaled down to fit into the image box
- All images maintain their aspect ratio, but some parts are clipped
img {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
object-fit: none;
}
object-fit: cover (most used)
- All images are scaled up or down to fit into the image box
- All images maintain their aspect ratio, but some parts are clipped

object-position
- As you can see in the above examples, images are centered (both horizontally and vertically) by default
- You can change the position with the
object-positionproperty, e.g:
img {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
object-fit: none;
object-position: top left;
}- The values for
object-position(see also interactive example) are the same as forbackground-position:- first value for vertical positioning:
top,center,bottomor use fixed units likepx,%, ... - second value for horizontal positioning:
left,center,rightor use fixed units likepx,%, ... - horizontal and vertical positioning values are interchangeable:
object-position: top left;=object-position: left top;
- first value for vertical positioning:
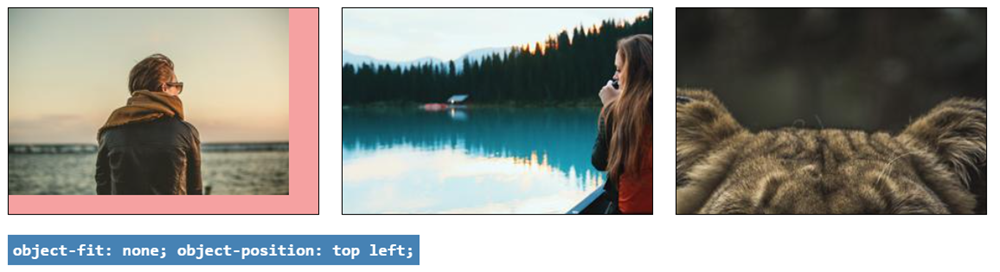
Example
Small screen (below 600px)
- All images are responsive
img {
width: 100%;
height: auto;
}Medium screen (between 600px and 800px)
- All images
- have a fixed
widthandheight - are cropped symmetrically (around the center/middle)
- have a fixed
img {
width: 125px;
height: 200px;
object-fit: cover;
}Larger screen (above 800px)
- All images are responsive again
img {
width: 45%;
height: auto;
}Oversized background image on body
Tips
Just as for images, you can also control the size/fit and positioning of background images
- For size/fit:
element sizing possible values image object-fitcontain,cover,fillandnonebackground image background-sizeonly containandcover(and values inpxor%)- For positioning:
element positioning possible values image object-positiontop,center,bottom,left,right,px,%,...background image background-positiontop,center,bottom,left,right,px,%,...
- The following example/exercise demonstrates how to set a fixed, oversized background image on the
body(or on thehtmlelement) - Let's start with a
background-colorand abackground-imageof800px*600pxon the body- As you now know from a previous chapter, the background will copy itself horizontally and vertically
- Open the pen below in full screen mode to see the effect
Exercise
- Follow these three steps to transform the background into a static, fullscreen background image
- Cover the background with the whole image:
background-size: cover;- Depending on the size of the browser window, you only see a small portion of the original image
- By default, you see the top left corner of the image
- Fix the background image (so it doesn't scroll with the content of the page) with
background-attachment: fixed; - Position the background image, e.g.
background-position: top center;
- Cover the background with the whole image:
REMARKS
- To limit the loading time of web pages, it is best practice not to use too large background images: background images must remain below 200kB
- Always make sure that the
background-colormatches the colour tones in thebackground-image, so that a suiting colour is shown when loading the page - If you study the CSS code in detail, you notice that the
divon the page gets aheightof110vhor 110% of the viewport height. As such, thedivis taller than the screen and a scrollbar will be shown. Read more on viewport units (viewport heightvh, viewport widthvw, ...) in CSS Viewport Units: A Quick Start.
| EMMET instruction | result |
|---|---|
bga + TAB | background-attachment: ; |
bga:f + TAB | background-attachment: fixed; |
bgp + TAB | background-position: 0 0; |
Filters
- One of the nice recent features in CSS3 is the addition of filters on images which reduces the need to use photo editing programs
- Some examples:
| function | values |
|---|---|
blur() | px |
brightness() | from 0% to 100% (or from 0 to1) |
contrast() | % |
grayscale() | from 0% to 100% (or from 0 to1) |
invert() | from 0% to 100% (or from 0 to1) |
opacity() | from 0% to 100% (or from 0 to1) |
saturate() | from 0% to 100% (or from 0 to1) |
sepia() | from 0% to 100% (or from 0 to1) |
hue-rotate() | ..deg |
drop-shadow() | hoff voff blur color |
Clipping path
- Another new, but not yet widely supported feature is
clip-path
- A good site to help you in creating such a
clip-pathis https://bennettfeely.com/clippy/- A number of sample images are used in combination with predefined shapes that you can adjust
- Keep a close eye on the dimensions of the image you want to clip
- The code you need to copy into CSS can be found at the bottom left
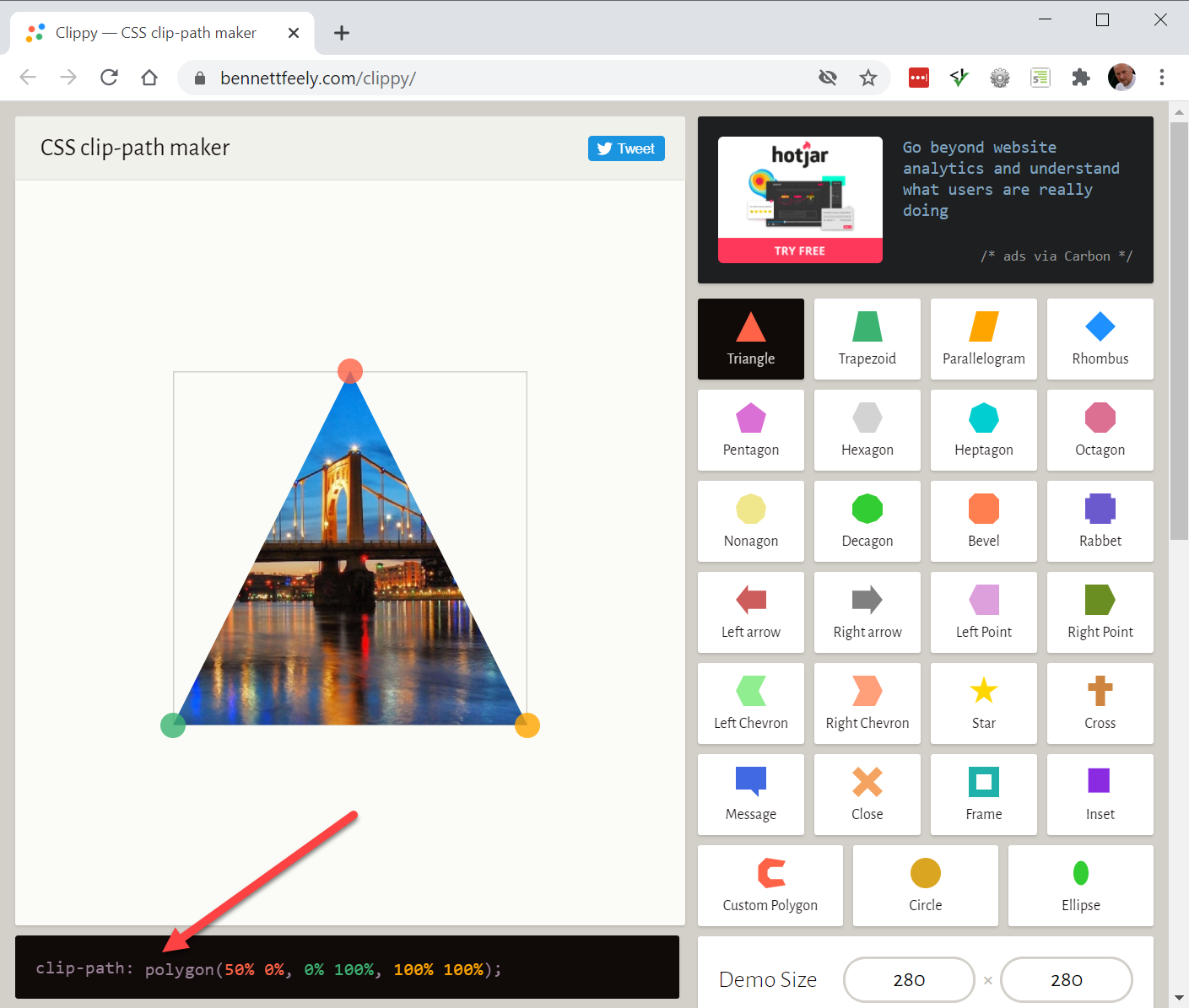
REMARK
For Safari users, the clip-path statement has to be preceded by a similar line with the vendor prefix -webkit, as this property is not yet fully supported by Safari. For example:
.t {
-webkit-clip-path: polygon(0 0, 100% 0, 100% 20%, 65% 20%, 65% 100%, 35% 100%, 35% 20%, 0% 20%);
clip-path: polygon(0 0, 100% 0, 100% 20%, 65% 20, 65% 100%, 35% 100%, 35% 20%, 0% 20%);
}